SOUND CARD For PC
A Sound Card for PC can be defined as an expansion card that is capable of producing sounds using certain computer programs. Hence, it can be also called an audio card. It is a peripheral device that can be attached to an ISA (or) PCI slot of a motherboard. The following are the functions of a sound card.
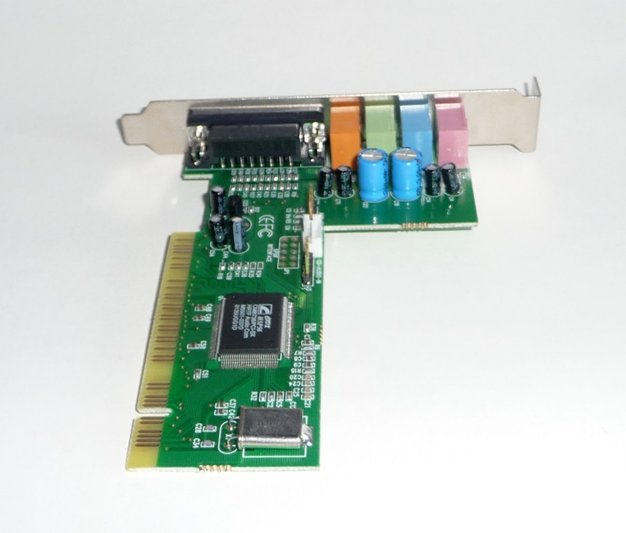

Audio Interface
(i) Synthesizing sounds
(ii) Used as MIDI interface
(ii) Converts analog-to-digital
(iv) Converts digital-to-analog
(i) Synthesizing Sounds
This refers to the process of generating sounds. Earlier components were capable of producing only a beep sound. But from the 1980s with the invention of special add-on cards called sound cards a variety of sounds could be synthesized. There are three methods that can be used for generating the sounds, they are Frequency Modulation (FM), wavetable, and physical modeling.
(ii) Analog Vs Digital
The best examples for analog and digital are the sounds and data of the computer respectively. Analog signals are a collection of waves that can traverse through the matter. Digital signals are nothing but electrical impulses containing O’s and 1’s. Hence a sound card can be used for converting computer digital data into analog data. For this purpose, it contains four components that are present on its printed circuit board. They are,
(a) Analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
(b) Digital-to-analog converter (DAC)
(c) ISA (or) PCI interface that can attach the sound card to the motherboard.
(d) Input and output connections for the microphone and speakers.
However, there are some sound cards that contain a CODEC chip (Coder/Decoder) instead of different ADC and DACs. This chip has the ability to carry out both conversions.
Working of ADC’s and DAC’s in a Sound Card
ADC Working:-
Assume that a user wants to record his voice on the computer. For this purpose, using a microphone he speaks. This microphone is connected to the sound card. Then the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) will convert the analog waves into digital data that the computer understands. This is done by sampling or digitizing the sound by considering some specific measures of the wave at regular intervals.
DAC Working:-
In order to play the sound that was recorded earlier ai DAC is used. The DAC would carry out the same steps in reverse order so as to play the sound through the speakers.
The number of measurements per second is known as the sampling rate. A card should possess a high sampling rate in order to obtain accurate waves. But high rates will also lead to a decrease in sound quality which is called distortion. There are two ways of measuring the reduction in sound quality. They are,
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
It can be represented in the form of a percentage( %)
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
It can be measured in terms of decibels
SOUND CARD STANDARDS
NAME | YEAR | SAMPLING FREQUENCY | AUDIO BITDEPTH | CHANNELS | TYPE |
| PCjr | 1984 | 122 Hz to 125 kHz | 16 volume settings | 3 square wave tone; 1 white noise | PSG |
| PC Speaker | 1981 | 6 bit | 1 pulse-width modulation | PWM | |
| MPU-401 | 1984 | 1 MIDI in; 2 MIDI out; DIN sync out; and tape sync IO; metronome out | MIDI | ||
| Tandy 1000 | 1984 | 122 Hz to 125 kHz | 16 volume settings / 6 bit | 3 square wave tone; 1 white noise; and 1 pulse-width modulation | PSG |
| Adl lib | 1987 | 49.716 kHz | 64 volume settings | 6-voice FM synthesizer, 5 percussion instruments | FM synthesizer |
| Covox | 1987 | 8 bit | 1 DAC | ||
| Roland Sound Canvas | 1991 | 32 kHz | 16 bit | 24 voices | |
| Roland MT-32 | 1987 | 32 kHz | 16 bit | 8 melodic channels; 1 rhythm channel | |
| Sound Blaster | 1989 | 22 kHz | 8 bit | 1 DAC; 11-voice FM synthesizer | FM synthesizer |
| AC97 | 1997 | 96 kHz | 20 bit | 6 independent output channels | PCM |
| Gravis Ultrasound | 1992 | 44.1 kHz | 16 bit | 16 stereo channels | |
| Intel High Definition Audio | 2004 | 192 kHz | 32 bit | up to 15 independent output channels | PCM |
| Environmental Audio Extensions | 2001 | 8 simultaneous 3D voices |



