MotherBoard of Computer
The motherboard is one of the most important and main parts of the computer. It handles all the components of the system together and transforms them into a personal computer. Generally, a motherboard is also called as the mainboard, system board, or planar. The motherboard is a large printed circuit board. It is the base to almost all important parts of the computer that includes a microprocessor, chipset. ache, memory sockets, expansion bus, parallel and serial ports, mouse and keyboard connectors and IDE, EIDE, or SCEI controllers.
In this, the role of the motherboard is to tie the operational components of the PC. Also, other device drivers such as printers, hard disks, CD-ROMs are connected or controlled by the controllers or devices located on the motherboard. The features of motherboards are unique from manufacture to manufacture. This increases the value of each motherboard as they can incorporate a few more controllers. expansion buses, processor sets, external connectors, and memory slots. Therefore, the consumers get a variety of choices for selecting the desired configuration of the PC that contains a motherboard with a long list of features. So, for this, the consumer must obtain complete information about the product they want to buy in order to and lower quality components. And usually, the upgrading of motherboard incurs high cost due to which most people prefer to buy new PC.
There are two different design approaches for PC mainboards or motherboards.
They are
1. Motherboard style
2. Backplane style.
1 Motherboard Style:
The motherboard is also known as a mainboard, or a system board or a planar. Its primary role is to assemble all basic. system components of PC on a single Printed Circuit Board (PCB). A PC’s electronic circuitry present in all the motherboard’s single board design arranges a channel that serves as a path to locate all the operations flows occurring on the motherboard
2. Backplane Style:
The mainboards of the backplane-style were in demand during the mid-to-late 1980s. But now they are less popular but are still manufactured. They are usually incorporated in large PC network servers and various other computers upon which frequent processor up-gradation is performed. Basically, the backplane mainboards have less storage capacity and less efficient in nature They are categorized into three types,
(a) Passive backplane
(b) Daughter boards
(c) Active backplane
COMPONENT LAYOUT OF MOTHERBOARD
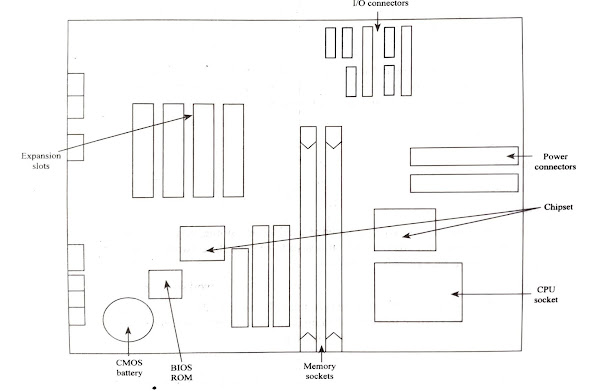
A motherboard can be defined as the base on which the PC will be built. It consists of various components that communicate with each other. The major component on a motherboard includes the following. Components on a Motherboard
1. CPU Slot and Socket
This component enables the CPU to be mounted onto the motherboard using socket (or) slot mounting..
2. Chipset
It can be defined as a component that consists of the circuitry and functions. .
3. Memory Sockets
These are the components that mount the memory of the PC onto the motherboard. It can be cither individual memory chips (or) memory modules
4. BIOS ROM
This component consists of the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) stored on a Read-Only Memory (ROM). The BIOS is responsible for turning ON the PC when power is supplied and it also connects the CPU to the PC’s peripherals
5. CMOS Battery
The CMOS battery is one of the components of the motherboard that is responsible for providing power supply to the CMOS memory unit that stores the configuration of the system, This is helpful during the booting of the system.
This component is used in order to provide a steady power supply to all the components present on the board. Different components on the board require different voltages of power supply
7. I/O Connectors
These components enable the CPU to connect to the external devices by carrying out communication.
These are necessary to connect the internal devices and external peripherals to the motherboard and CPU. This connection is achieved by the expansion bus.